Cities and Temples
Click on the locations below to learn more about ancient Egyptian cities, temples, and tombs.
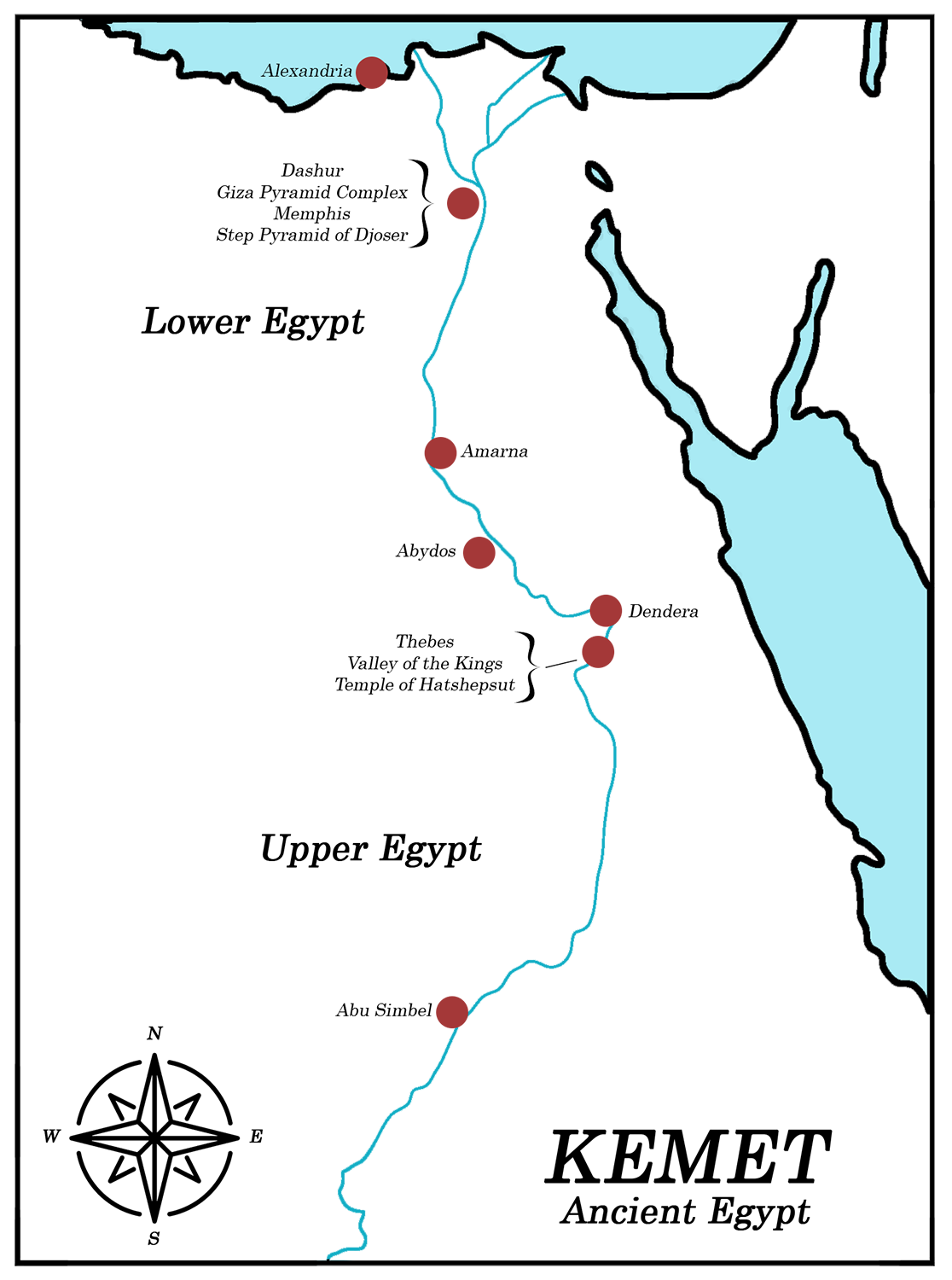
Alexandria

Founded in c. 331 BCE by Alexander the Great, Alexandria served as the capital of Egypt until it surrendered to Arab forces in 642 CE. Much of Alexandria is underwater today, but it once boasted the Library of Alexandria, one of the largest libraries in the world, as well the Lighthouse of Alexandria, which is considered an ancient wonder of the world.
Dashur, Giza Pyramid Complex, Memphis, and Step-Pyramid of Djoser
 |
 |
Dashur
Dashur, named after the nearby village of Manshiyyat Dashur, encompasses several pyramids, built during the Old and Middle Kingdoms. Among others, these include the Bent and Red Pyramids of Sneferu, and both the Black and White Pyramids, built by Middle Kingdom Pharaohs Amenemhat II and III respectively.
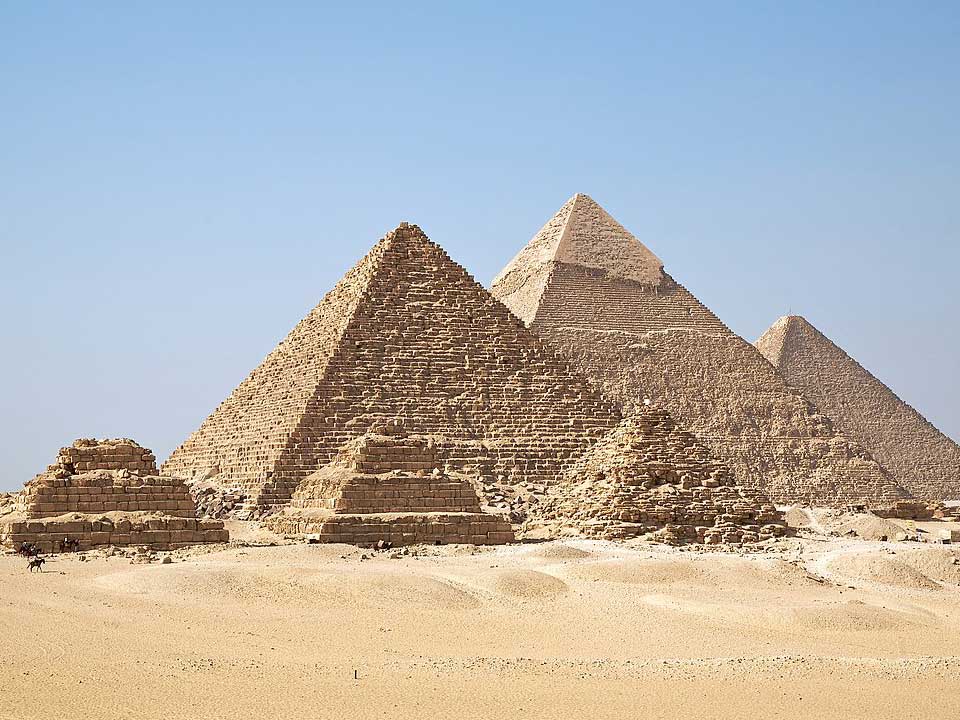
Giza Pyramid Complex
This complex includes three large pyramids, a collection of smaller pyramids called Queen’s Pyramids, the Great Sphinx, and the surrounding cemetery and temples. All built during the Fourth Dynasty, in the Old Kingdom, the largest, northern pyramid was constructed by the pharaoh Khufu, the middle was constructed by the pharaoh Khafre, and the southern pyramid was constructed by the pharaoh Menkaure. It is unknown when the Great Sphinx was built, or by whom, but evidence suggests it has been recarved and repurposed, perhaps more than once.
Memphis
Memphis was a prominent Egyptian city and necropolis, that served as during the Early Dynastic Period and the Old Kingdom, but later retained relevance as a hub for education, and because of its proximity to ancient burial structures, and to the capital created by Rameses II, Pi-Ramses. Memphis contains the burial structures at Saqqara, the Giza Pyramid Complex, and more.
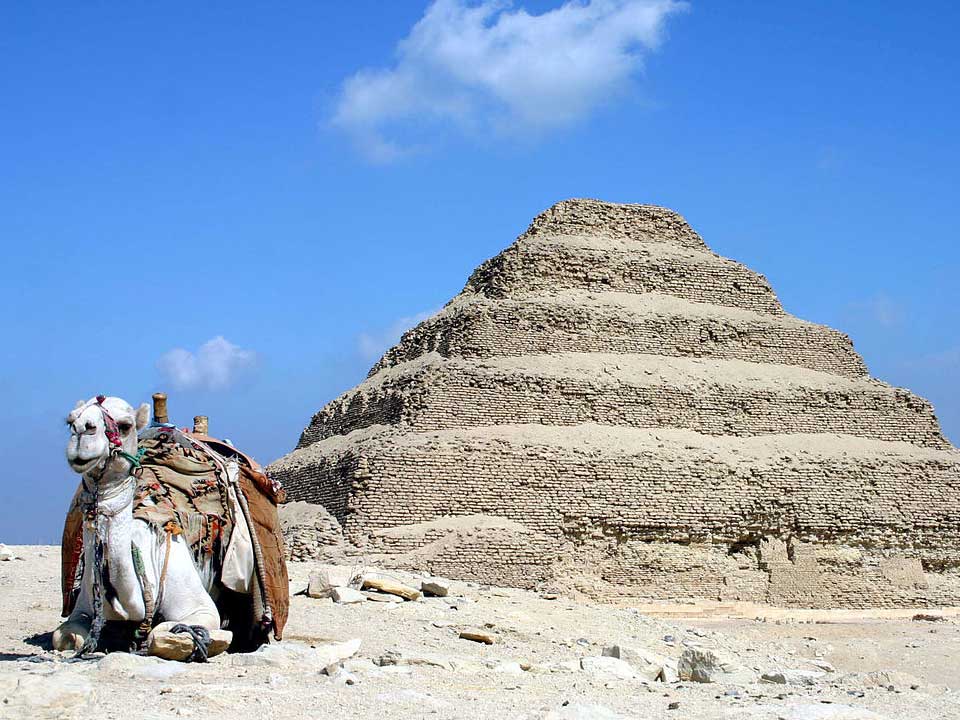
Step-Pyramid of Djoser
Consisting of stacked mastabas, the Step-Pyramid of Djoser is the first of Egypt’s pyramids. It was built by the architect and priest Imhotep in the Fourth Dynasty, and marked a shift towards elaborate tomb-building for Egypt’s elite.
Amarna

Known in antiquity as Akhetaten, Amarna is the modern name for the city founded by the Heretic King, Akhenaten. In the New Kingdom, he uprooted the Egyptian capital from Thebes, abandoned the national religion, and moved to Tell el-Amarna to worship Aten, the disk of the sun. The city was abandoned after his death.
Abydos
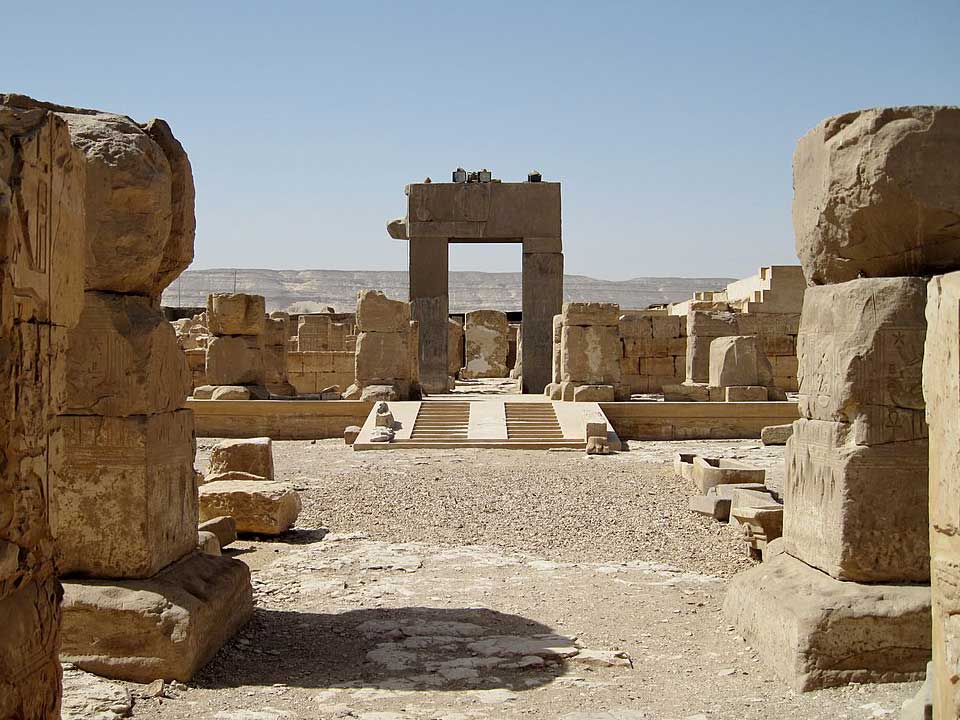

Also a functioning city, Abydos was a vast burial site. It includes temples and graves from pre-dynastic Egypt, and was used all the way into the Roman period. Notably, it includes the tomb of the first pharaoh, Narmer, and the mortuary complex of the New Kingdom pharaoh Seti I.
Thebes, Valley of the Kings, and Temple of Hatshepsut
 |
 |
Thebes
The ancient city of Thebes operated as the capital of Egypt in the Middle and New Kingdoms. On the eastern bank of the Nile, it includes the Luxor Temple Complex, the possible location where many pharaohs were said to have been crowned, and the Karnak Temple Complex (c. 1970 BCE), a religious center for the worship of the god Amun.
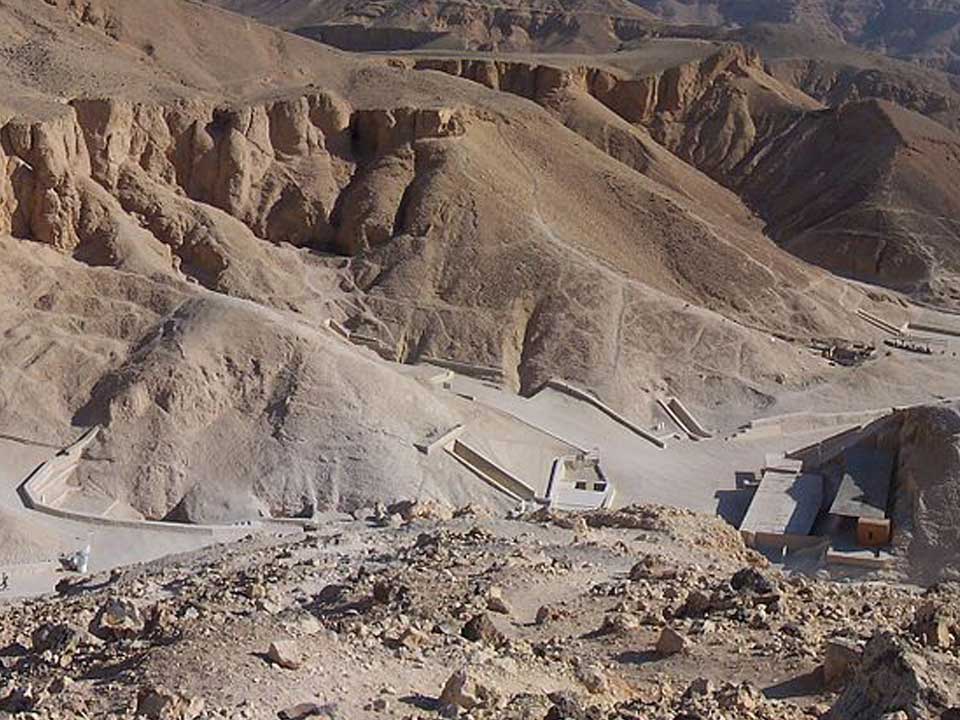
Valley of the Kings
Located in close proximity to one another are two vast burial sites, one for the kings and nobles of the 18th, 19th, and 20th Dynasties, and one for their queens, princesses, and princes. The Valley of the Kings includes the underground tombs of Tutankhamun, Akhenaten, and Ramses II. The Valley of the Queens includes Sitre (wife of Ramses I and mother of Seti I), Tuya (wife of Seti I and mother of Ramses II), and Nefertari (wife of Ramses II).
Temple of Hatshepsut
Constructed by one of Egypt’s most famous woman pharaoh, Hatshepsut, this temple was carved in-part into the cliffs of Deir el-Bahari. It is considered a masterpiece of ancient architecture, with three massive terraces that include shrines to Hathor and Anubis, and reliefs that portray Hatshepsut’s military conquests and reinforce her divine claim to the throne.
Dendera
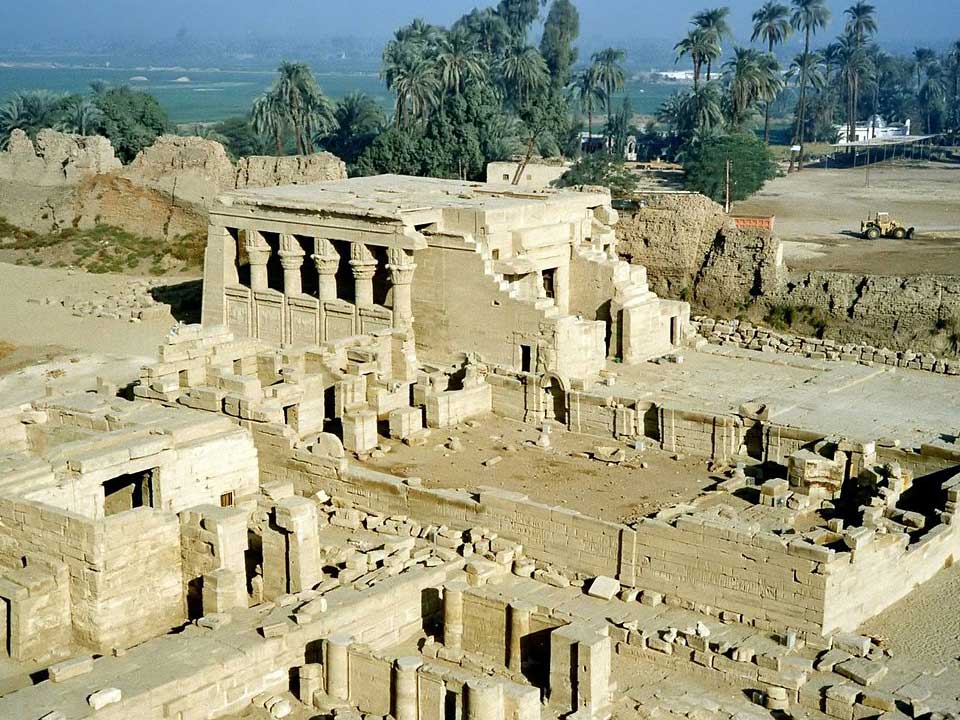

One of the best-preserved ancient temple complexes in Egypt, Dendera contains temples to Hathor and Isis, among others. The Temple of Hathor dates back to Middle Kingdom Egypt, but other structures were added as late as the Ptolemaic Period.
Abu Simbel
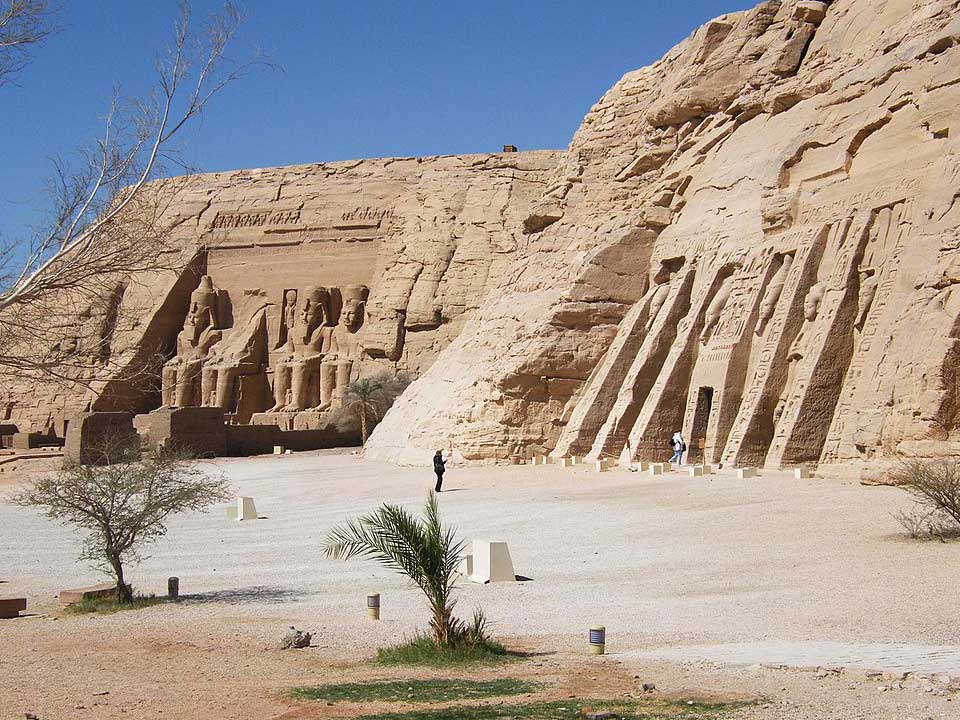

Built during the reign of Ramses II, this complex of temples was intended to establish the might of Egypt in newly-conquered Nubian lands. In 1968, the entire structure was deconstructed brick by brick and rebuilt on higher ground to escape flood caused by the construction of the Aswan Dam.


